Remove First
- Removes first element (element referenced by head) from linked list
public Node removeFirst() {
}Case: Linked List is empty
Simply return null as there is no element to delete.
public class LinkedList {
public Node removeFirst() {
if (length == 0) {
return null;
}
}Case: Linked List is not empty
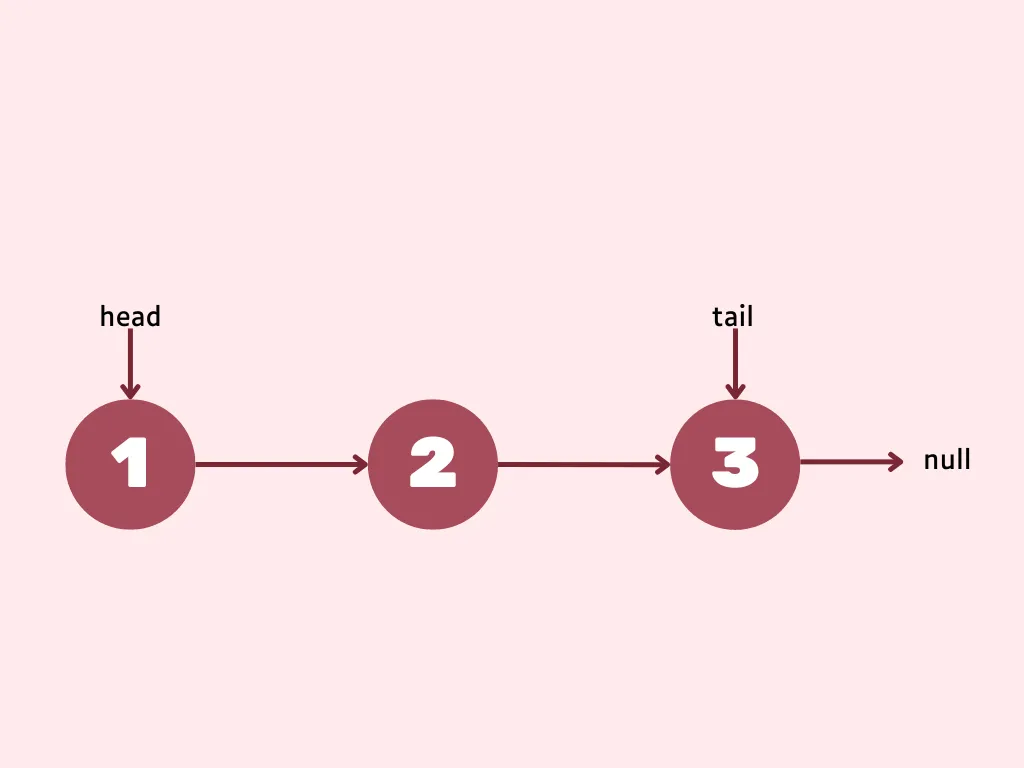
public Node removeFirst() {
if (length == 0) {
return null;
}
Node temp = head;
head = head.next;
temp.next = null;
length--;
if (length == 0) { // means linked list had length 1
tail = null;
}
return temp;
}head = head.next points the head to its next node as you need to remove first node (fyi if length is 1 then head = null).
temp.next = null temp references to first node, so setting temp’s next to null will remove it from linked list.
length-- decrement the linked list as you removed element.
You also need to handle one edge case when linked list has length 1. In such case simply set tail to null.
Testing
public class LinkedListTest {
@Test
void removeFirst() {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
// remove from empty linked list should return null
assertNull(linkedList.removeFirst());
// remove when list consists one element
linkedList.append(1);
linkedList.removeFirst();
assertEquals(0, linkedList.getLength());
// remove on list with length greater than one
linkedList.append(1);
linkedList.append(2);
linkedList.append(3);
linkedList.append(4);
var temp = linkedList.removeFirst();
assertEquals(3, linkedList.getLength());
assertEquals(1, temp.getValue());
assertEquals(List.of(2, 3, 4), convertToArrayList(linkedList));
}
}Time complexity
Removing an element from the end of a linked list has linear worst-case time complexity - O(1) as you need only need to perform constant operation.