Prepend
- Adds element at the beginning of linked list
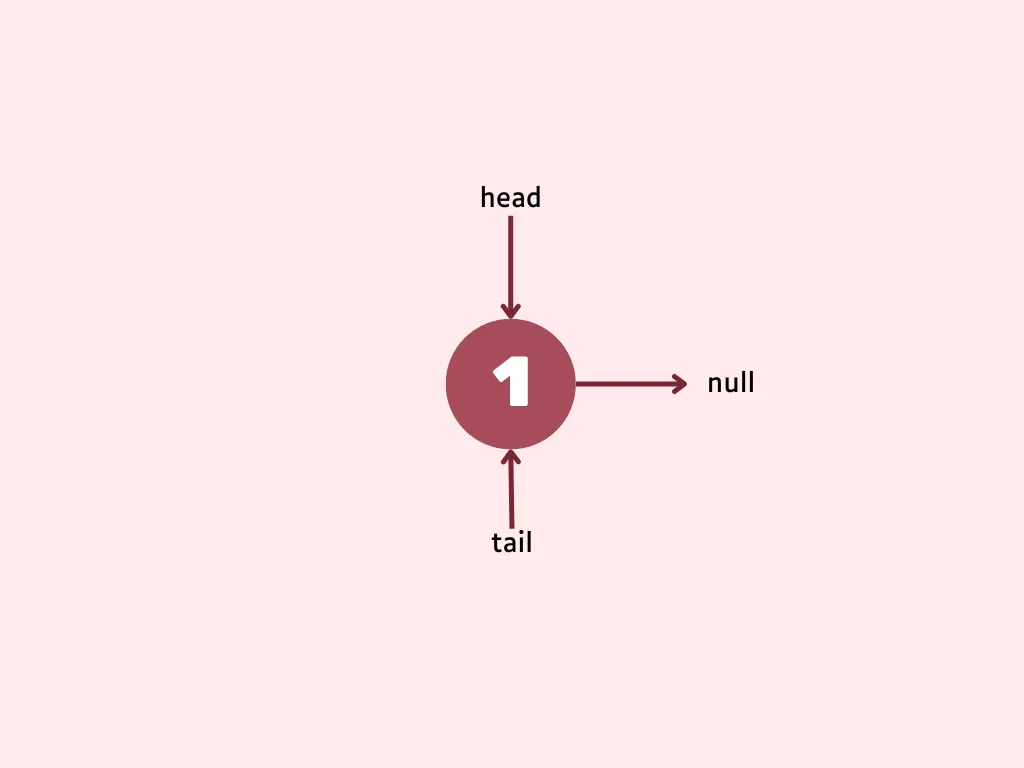
Case: Linked List is empty
You simply need to create a new node with provided value and point head and tail to the created node. Since you added a node, increment the linked list as well.
public class LinkedList {
public Node prepend(int value) {
// Create new node from given value
Node node = new Node(value);
if (length == 0) {
head = node;
tail = node;
}
length++;
return node;
}
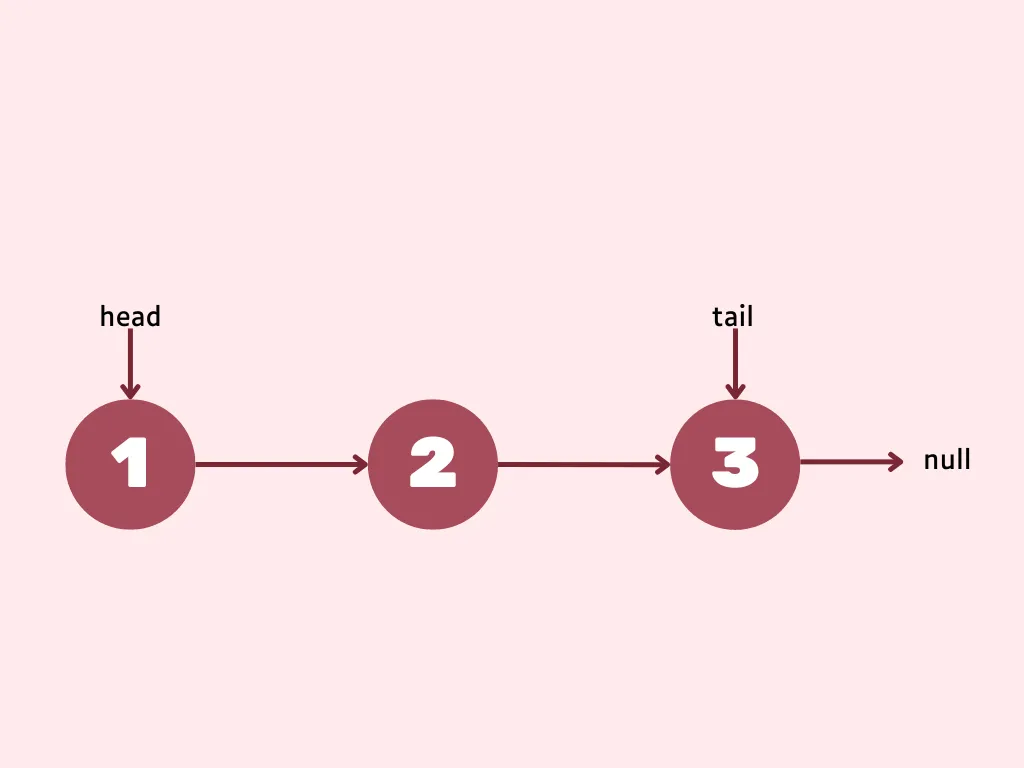
}Case: Linked List is not empty
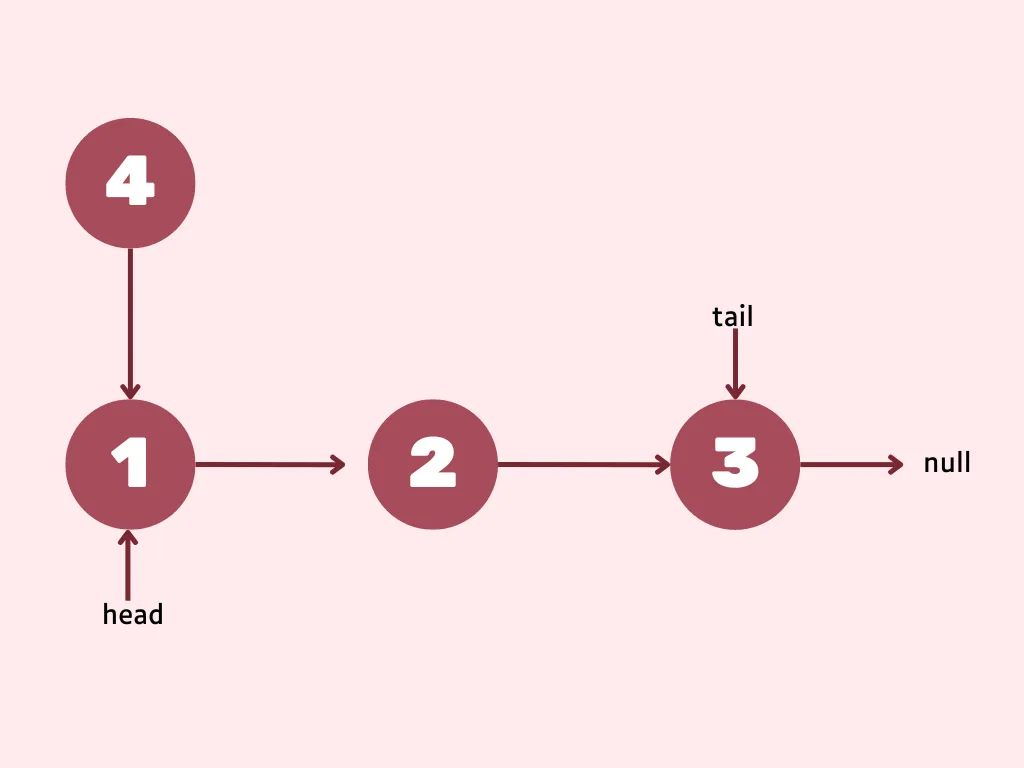
First you need to point the new node to first node. For this simply set the newly created node’s next reference to what the head is referencing.
node.next = head;Head should always reference to first node, so point head to newly added node.
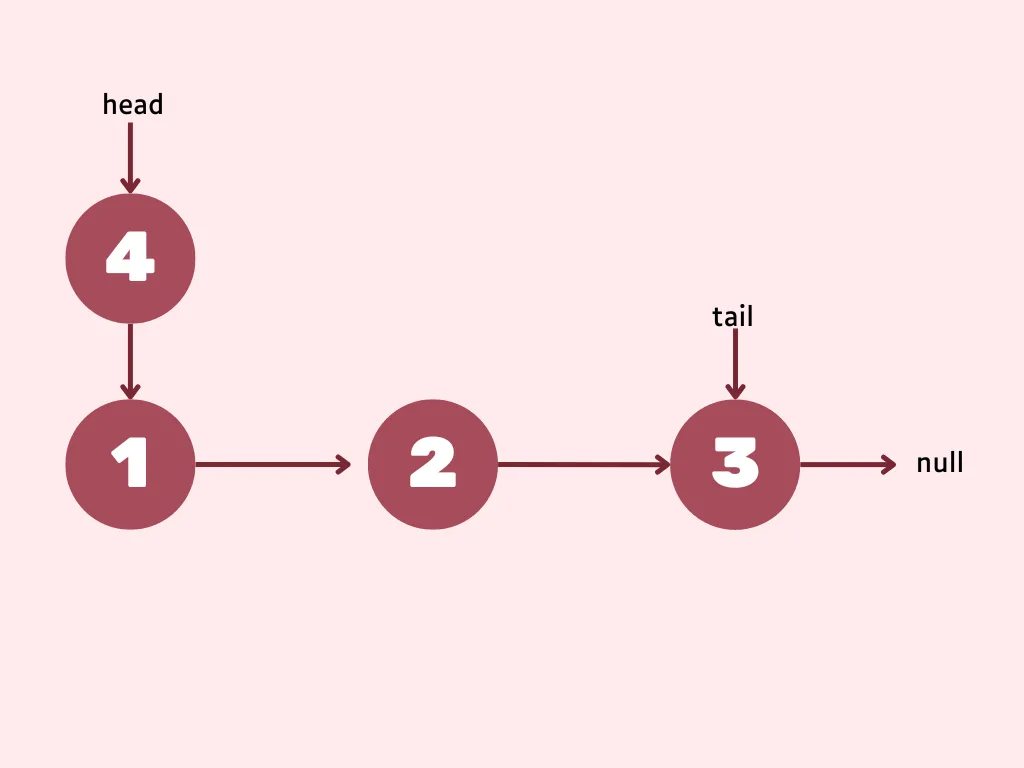
head = node;public class LinkedList {
public Node prepend(int value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
if (length == 0) {
head = node;
tail = node;
}
node.next = head;
head = node;
length++;
return node;
}
}Testing
public class LinkedListTest {
@Test
void prepend() {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.prepend(1); // prepend when length equals 0
assertEquals(1, linkedList.getLength());
assertEquals(List.of(1), convertToArrayList(linkedList));
linkedList.prepend(2); // prepend when length greater than 0
linkedList.prepend(3);
linkedList.prepend(4);
assertEquals(4, linkedList.getLength());
assertEquals(List.of(4, 3, 2, 1), convertToArrayList(linkedList));
}
}Time complexity
Prepending a node to a linked list is a constant operation so, it has a worst-case time complexity - O(1).